Technical library
Items 1-12 of 286 Results
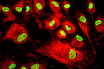
During the isolation of our Human Mononuclear Cells (hMNC), we first of all pay attention to thoroughly discard the platelet-containing fraction before we aspirate the MNC containing-interphase of the Ficoll gradient. The harvested MNC fraction is then subjected to several washing steps to remove potential remaining platelets. Finally, the cell preparations are verified by microscopy to be largely free of platelet contamination.
There is a strong variation from donor to donor and sometimes from donation to donation concerning the number of vials that can be produced. This is due to individual variances between the donors as some of them have more MNCs per ml of blood and others have less. Generally, the number of vials (each with 25 x 106 cryopreserved cells) per lot ranges between 10 and 40.
Choosing a suitable culture medium is crucial factor for in vitro cell cultivation and significantly affects the success of cell culture experiments, from the first step of development and when transitioning to clinical applications. Due to specific requirements of primary cells and each researcher’s application, we provide a wide range of advanced media formulations.
Therefore, it is essential for researchers to have a clear understanding of how to define the specifications of our cell culture media and reagents, from serum-free or xeno-free to chemically defined, to estimate and understand the associated implications for their intended applications. We can support you by providing a comprehensive guideline for the characterization and qualification of our cell culture media and reagents.
Discover and download our Media & Reagents Specification Guide
Without cytokines, the macrophages will die very quickly. You must supplement the Macrophage Base Medium XF (Bsal Medium + SupplementMix) with the appropriate cytokines or at least with human AB serum.
Our Primary Cancer Culture System (PCCS, C-28081) supports Cancer Stem Cells universally, therefore the PCCS can also be used for CSCs from blood cancer/leukaemia.
However, we recommend not to treat the surface of the culture vessel with NCCD reagent, but to add 12.5 µl NCCD/ml to the PCCS and seed the cells into the medium.
Yes, our cancer media (Primary Cancer Culture System/PCCS, 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF, Cancer Cell Line Medium XF) also support the growth of murine tumor cells.
Yes, it is. The Primary Cancer Culture System (C-28081) is very selective for cancer stem cells – any other cells will be eliminated after a short time.
App Note: Isolation of patient-derived cancer stem cellsIn our Primary Cancer Culture System (PCCS, C-28081), only the malignant tumor cells can survive. Therefore, benign animal cells (e.g., fibroblasts) will be depleted and the malignant human tumor cells will survive.
Alcian Blue stains the extracellular matrix of chondrocytes, e.g. cartilage-specific aggrecan and other glycosaminoglycans. To our knowledge, chondrocytes only express aggrecans when grown in 3-D culture and not in 2-D culture. To detect cartilage specific markers in monolayer culture, it is recommended to perform immunofluorescence detection of collagen type II.
Our skeletal muscle cells are mainly isolated from M. pectoralis, sometimes also from M. gastrocnemius, M. intercostales or M. gluteus maximus. The exact localization is specified in the Certificate of Analysis.
Our TNS solution contains 0.05% (w/v) trypsin inhibitor from soy bean in HepesBSS/0.1% BSA.
Yes, you can aliquot the SupplementMix upon delivery and freeze down 2 or 4 individual aliquots at -20°C. This way, you can prepare smaller volumes (2 x 250 ml or 4 x 125 ml) of complete culture medium and thus extend the time you can use the medium.