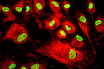
Technical library
Items 25-36 of 289 Results
In principle, both types of liquid nitrogen storage are acceptable, each having its advantages and disadvantages.
- Liquid phase storage provides a consistent temperature of -196°C, a longer holding time and a greater vial capacity but involves the risk of contamination issues.
- Storage in the gas phase is very safe with respect to contaminations but the holding time of the cells is shorter and the vial capacity is reduced.
Our chondrocytes are derived from patients (~55-80 years) who underwent surgery for total endoprothesis of the hip or knee joint. In most cases this is necessary due to arthrosis. If the tissue shows macroscopic lesions, it is not used for cell isolation.
The amount of media needed per vial depends on the growth characteristics of the cells, the size of the TC vessels and the split ratios used, the frequency of media changes, the type of experiments you perform, etc. It is therefore difficult to give definite quantities. As a rough guideline, 1-2 bottles (500 ml each) are needed for 1 vial of HUVEC.
PromoCell's Osteoblast Basal Medium is an optimized media formulation developed for human osteoblast culture. The exact composition is proprietary.
Generally, you can split differentiated adipocytes. But these cells lose their ability to proliferate after differentiation and you can't expand the culture any more. Therefore it is recommended to plate the cells into the needed vessels (e.g. multiwell plates) prior to induction of differentiation so that trypsinization isn't necessary.
HFDPC are isolated from the hair papilla of normal human scalp hair follicles. Hair papilla in the adult hair follicle play a crucial role in the dermal-epidermal interactions that control hair production and in hair growth cycle events. The follicle dermal cells are cryopreserved at second passage and can be cultured for at least 10 population doublings when using PromoCell Follicle Dermal Papilla Cell Growth Medium (Cat. C-26501). Typical population doubling times are between 20-36 hrs. The recommended seeding density after thawing/trypsinization is 5,000-10,000 cells/cm2. Using 1:4 splits, you can perform 4-5 passages with the cells.
Typical cell densities are between 32,000 - 40,000 cells/cm² (approx. 800,000 - 1 million cells per T25-flask).
If you purchase a proliferating culture of human osteoblasts (C-12760), there will be > 500,000 cells in the TC-flask. Once the culture is subconfluent, you will count between 750,000 - 1.1 million cells/T25 (depending on the cell lot).
Our Osteoblast Growth Medium (C-27001) consists of the Basal Medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) FCS, but with no recombinant growth factors. The medium primarily supports the proliferative capacity of normal human osteoblasts. It does not contain osteogenic factors (like dexamethasone and beta-glycerophosphate) that promote differentiation, as many users test their own chemical compounds (growth factors, hormones), or examine the effects of physical strain or sheer stress on the differentiated functions.
The Osteoblast Growth Medium is well-suited as the basis for these applications and can be supplemented with further growth factors if necessary. To specifically induce mineralization, we supply Osteoblast Mineralization Medium (C-27020).
Induction of differentiation:
- Grow the cells in Preadipocyte Growth Medium (C-27410) until they reach complete confluence; this roughly takes 1 week. Change medium 2-3x per week.
- Aspirate the Growth Medium; add Preadipocyte Differentiation Medium (C-27437) for 72 h
- Aspirate the Differentiation Medium, add Adipocyte Nutrition Medium (C-27438).
The cells will now start to accumulate droplets of lipids which can be visualized under the microscope. The process usually takes 1-2 weeks. Change medium 2-3x per week. It is possible to maintain the differentiated adipocytes in Nutrition Medium for up to 4 weeks. However, the cells tend to lyse and detach after about 3 weeks.
Please note: We recommend to perform differentiation experiments at population doubling numbers lower than 4-5 (a maximum of 1 passage after thawing) in order to obtain a high differentiation level of the culture.
Our juvenile HDMEC (C-12210) are isolated from foreskin of young male donors (1-10 years). In contrast, adult HDMEC (C-12212) are derived from different skin localisations like the cheek, temple, or breast. The donors are > 20 years old and are mostly female. Adult HDMEC are the cells of choice when you need cells from a particular part of the body (other than foreskin), or if it is important for your study to use cells from female and/or adult donors.
a) HNEpC (Human Nasal Epithelial Cells) are isolated from nasal mucosa b) HTEpC (Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells) from the surface epithelium of trachea c) HBEpC from the surface epithelium of bronchie, and d) HSAEpC (Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells) from the distal portion of the respiratory tract in the 1 mm bronchiole area (comprising the cells from bronchioli and alveoli).